Author: Jason Beattie
Transit routing in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) using Dynamic Routing Gateways (DRGs), involves setting up a network architecture that enables communication between different virtual cloud networks (VCNs) or between on-premises networks and VCNs.
DRGs are used to facilitate this communication by providing a centralized point for managing routing between networks.
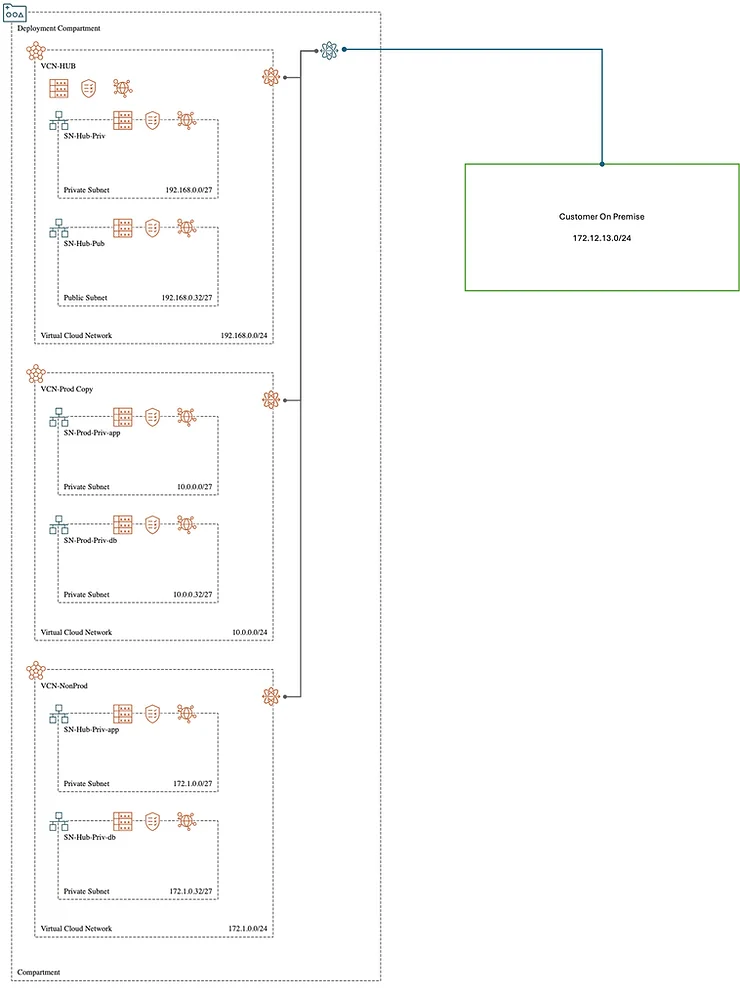
Below is a detailed guide based upon the above design:
1. Create Three Virtual Cloud Networks (VCNs):
VCN-Hub – 192.168.0.0/24
SN-Hub-Priv – 192.168.0.0/27
SN-Hub-Pub – 192.168.0.32/27
RT-Private-Hub
RT-Pub-Hub
VCN-Prod – 10.0.0.0/24
SN-Hub-Priv-app – 10.0.0.0/27
SN-Hub-Priv-db- 10.0.0.32/27
RT-Private-Prod-app
RT-Private-Prod-db
VCN-NonProd – 172.1.0.0/24
SN-Hub-Priv-app – 172.1.0.0/27
SN-Hub-Priv-db – 172.1.0.32/27
RT-Private-NonProd-app
RT-Private-NonProd-db
2. Create a DRG in the hub VCN.
3. Create a DRG attachment in all three VCNs and attach it to the DRG in the Hub VCN.
a. DRG-HUB-Att
b. DRG-Prod-Att
c. DRG-NonProd-Att
4. In the Hub Route Table (RT-Private-Hub) create the following Rules:
a. Prod-app – 10.0.0.0/24 – DRG-HUB
b. Prod-db – 10.0.0.32/24 – DRG-HUB
c. NonProd-app – 172.1.0.0/24 – DRG-HUB
d. NonProd-db – 172.1.0.32/24 – DRG-HUB
e. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24
5. In the Hub Route Table (RT-Pub-Hub) create the following Rules:
a. Prod-app – 10.0.0.0/24 – DRG-HUB
b. Prod-db – 10.0.0.32/24 – DRG-HUB
c. NonProd-app – 172.1.0.0/24 – DRG-HUB
d. NonProd-db – 172.1.0.32/24 – DRG-HUB
e. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24
6. In the NonProd-App route table (RT-Private-NonProd-app) create the following Rules:
a. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.0/24 – DRG-NonProd-Att
b. Hub-VCN- 192.168.0.0/27 – DRG- NonProd-Att
c. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.32/27 – DRG – NonProd-Att
d. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24 – DRG – NonProd-Att
7. In the NonProd-db route table (RT-Private-NonProd-db) create the following Rules:
a. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.0/24 – DRG-NonProd-Att
b. Hub-VCN- 192.168.0.0/27 – DRG-NonProd-Att
c. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.32/27 – DRG-NonProd-Att
d. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24 – DRG – NonProd-Att
8. In the Prod-App route table (RT-Private-Prod-app) create the following Rules:
a. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.0/24 – DRG-Prod-Att
b. Hub-VCN- 192.168.0.0/27 – DRG-Prod-Att
c. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.32/27 – DRG-Prod-Att
d. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24 – DRG –Prod-Att
9. In the Prod-db route table (RT-Private-Prod-db) create the following Rules:
a. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.0/24 – DRG-Prod-Att
b. Hub-VCN- 192.168.0.0/27 – DRG-Prod-Att
c. Hub-VCN – 192.168.0.32/27 – DRG-Prod-Att
d. On-Premise – 172.12.13.0/24 – DRG –Prod-Att
10. In the route table section of the DRG, create a route table labled RT-Hub and add the following rules:
a. 192.168.0.0/27 – SN-Hub-Priv – Next hop DRG-HUB-Att
b. 192.168.0.32/27 – SN-Hub-Pub – Next hop DRG-HUB-Att
c. 10.0.0.0/24 – VCN-Prod – Next hop DRG-Prod-Att
d. 172.1.0.0/24 – VCN-NonProd – Next hop DRG-NonProd-Att
e. 172.12.13.0/24 – On-Premise – Next hop DRG-HUB-Att
11. Update the DRG route table of the Hub-VCN attachment to use the “RT-Hub” DRG route table.
12. Create the Customer Premise Equipment (CPE).
13. Create the Site-to-Site VPN (IPSEC) Tunnels to the on-premise firewalls as required.
14. To test the paths are working, add a security list or NSG rule that will allow egress and ingress into each resource or subnet.
i.e. add ICMP and test ping works from on premise to a IP within the OCI spokes (Prod or NonProd)
I hope you find my blog post on transit routing helpful! It worth noting that testing the above in a test or sandbox environment is heavily recommended.
Interested to know more?
We’d be more than happy to discuss your requirements or questions, please get in touch here.
Contact us today to arrange an assessment or email:

Jason Beattie
Senior Architect at Vertice




